Imagine controlling devices, communicating, or even restoring lost functions using only your thoughts. This is the promise of Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI), a revolutionary technology that bridges the gap between the human brain and external devices. From healthcare to gaming, BCIs are transforming how we interact with technology and opening up new possibilities for human potential. This article delves into the science behind BCIs, their applications, and the challenges they face.
1. What Are Brain-Computer Interfaces?
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) are systems that enable direct communication between the brain and external devices.
- How They Work:
- Signal Acquisition: BCIs use sensors to detect brain activity, such as electroencephalography (EEG) or implanted electrodes.
- Signal Processing: Advanced algorithms interpret brain signals and translate them into commands.
- Device Control: The processed signals are used to control computers, prosthetics, or other devices.
- Types of BCIs:
- Invasive: Implanted directly into the brain for high precision (e.g., Neuralink).
- Non-Invasive: Wearable devices that sit on the scalp (e.g., EEG headsets).
- Partially Invasive: Placed inside the skull but not directly in brain tissue.
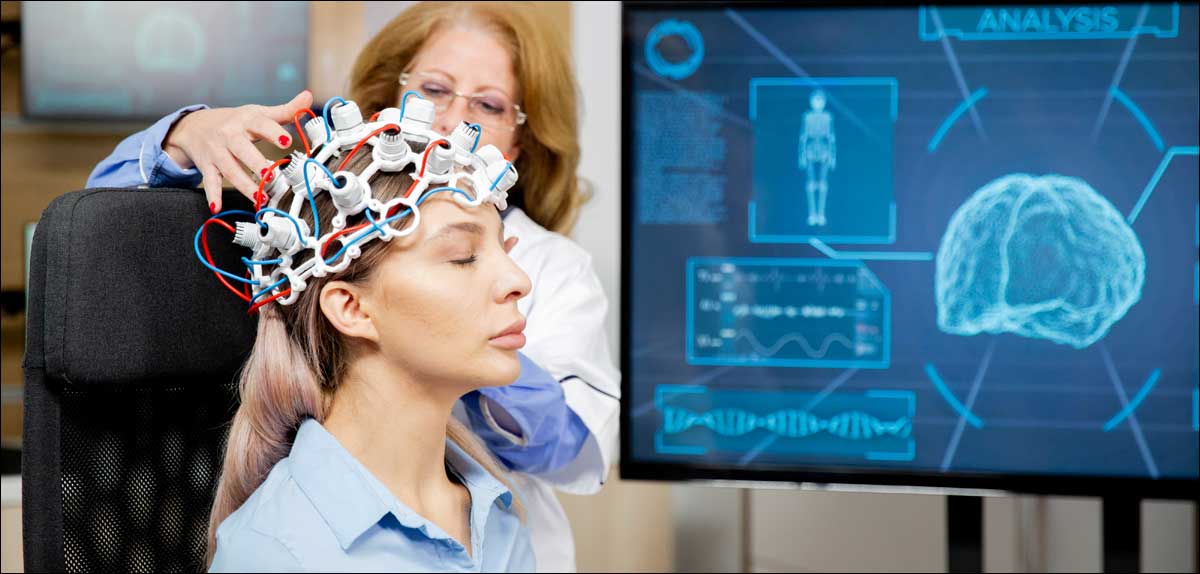
2. Applications of BCIs
BCIs are being used in a variety of fields, from healthcare to entertainment.
- Healthcare and Rehabilitation:
- Restoring Mobility: BCIs enable paralyzed individuals to control robotic limbs or wheelchairs using their thoughts.
- Treating Neurological Disorders: BCIs are being used to manage conditions like epilepsy, Parkinson’s, and depression.
- Communication for the Disabled: BCIs allow people with severe disabilities to communicate through text or speech synthesis.
- Gaming and Entertainment:
- Immersive Experiences: BCIs enhance virtual reality (VR) and gaming by allowing users to control actions with their minds.
- Emotion Detection: BCIs can adapt games or content based on the user’s emotional state.
- Military and Defense:
- Enhanced Training: BCIs are used to improve focus and decision-making in soldiers.
- Drone Control: Piloting drones or robots using brain signals for remote operations.
- Everyday Life:
- Smart Home Control: Using BCIs to operate lights, appliances, and other devices.
- Cognitive Enhancement: Improving memory, focus, and learning through neurofeedback.
3. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite their potential, BCIs face significant technical, ethical, and societal challenges.
- Technical Challenges:
- Signal Accuracy: Non-invasive BCIs often struggle with low signal resolution, while invasive BCIs carry health risks.
- Adaptability: BCIs must adapt to the unique brain patterns of each user.
- Latency: Delays in signal processing can hinder real-time applications.
- Ethical Concerns:
- Privacy: BCIs could potentially access and share sensitive neural data.
- Autonomy: The risk of misuse, such as manipulating thoughts or behaviors.
- Accessibility: Ensuring BCIs are affordable and available to all, not just the wealthy.
- Societal Impact:
- Job Displacement: BCIs could automate tasks, leading to job losses in certain sectors.
- Human Identity: The integration of technology with the brain raises questions about what it means to be human.
4. The Future of BCIs
The future of BCIs is filled with exciting possibilities and ongoing advancements.
- Key Trends:
- Miniaturization: Smaller, more portable devices for everyday use.
- AI Integration: Combining BCIs with AI to enhance signal processing and adaptability.
- Neural Implants: Advances in biocompatible materials for safer, long-term implants.
- Potential Breakthroughs:
- Mind-to-Mind Communication: Direct brain-to-brain communication for instant sharing of thoughts and ideas.
- Cognitive Enhancement: Using BCIs to boost memory, learning, and problem-solving abilities.
- Curing Disabilities: Restoring vision, hearing, or motor functions through neural interfaces.

Brain-Computer Interfaces represent the next evolution in human-technology interaction, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance our lives and overcome physical limitations. While challenges remain, the rapid advancements in BCI technology promise a future where the boundaries between mind and machine blur, unlocking new realms of human potential. As we move forward, it’s crucial to address ethical concerns and ensure that this transformative technology benefits all of humanity.
